有了 Promise 後應盡量避免使用 Nested Callback,但並不表示 Nested Promise 也不好,有些需求剛好適合 Nested Promise。
Version
macOS Catalina 10.15.4
VS Code 1.44.0
Quokka 1.0.285
ECMAScript 2017
Nested Callback
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
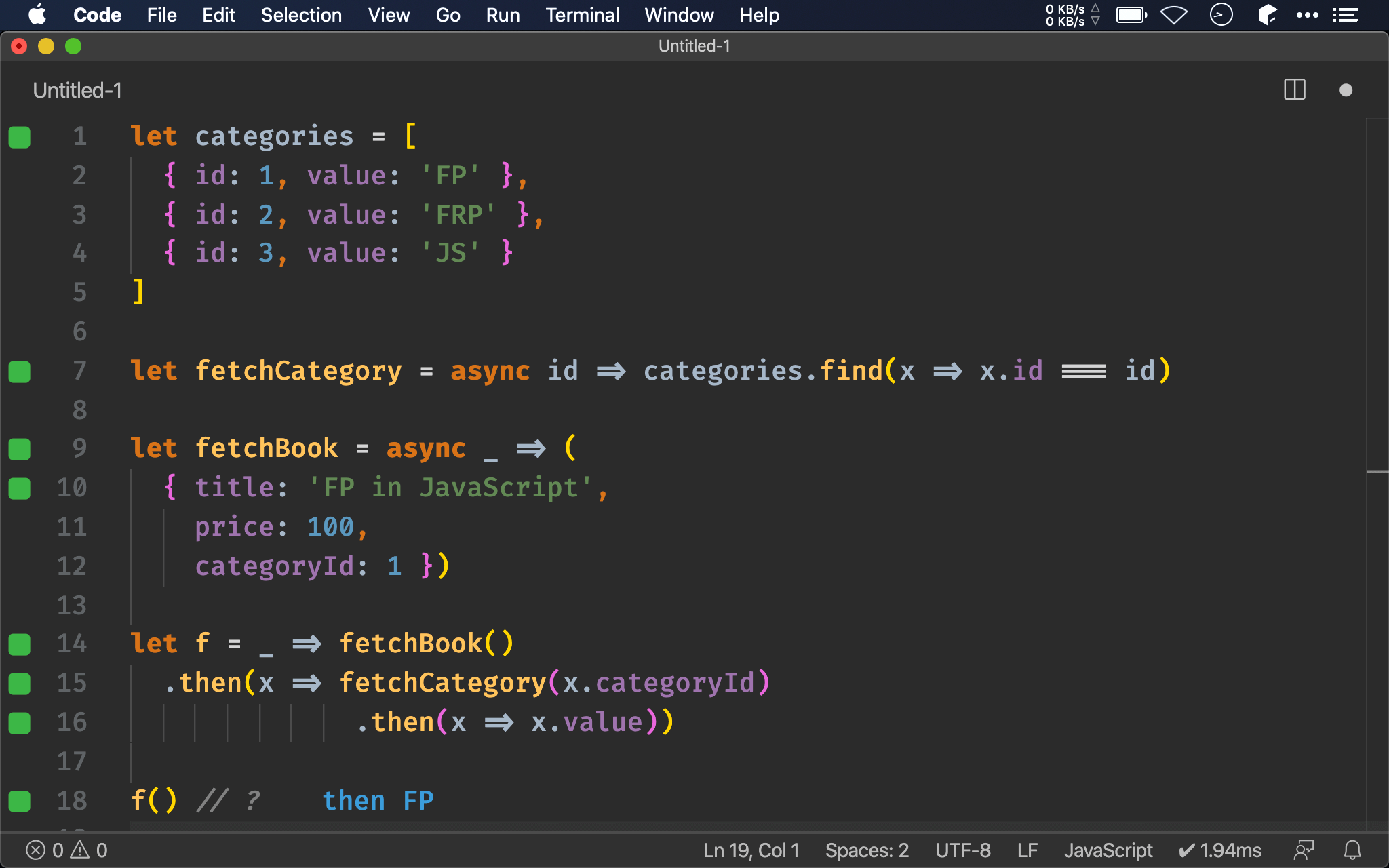
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
.then(x => x.value))
f() // ?
第 9 行
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
模擬 RESTful API 只回傳 categoryId。
第 7 行
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
若要取得 category,還要呼叫另外一個 API。
14 行
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
.then(x => x.value))
由於 then() 也是傳入 function,初學者常把 Promise 當 callback 使用,而寫成 nested callback。
Flatten Promise
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId))
.then(x => x.value)
f() // ?
14 行
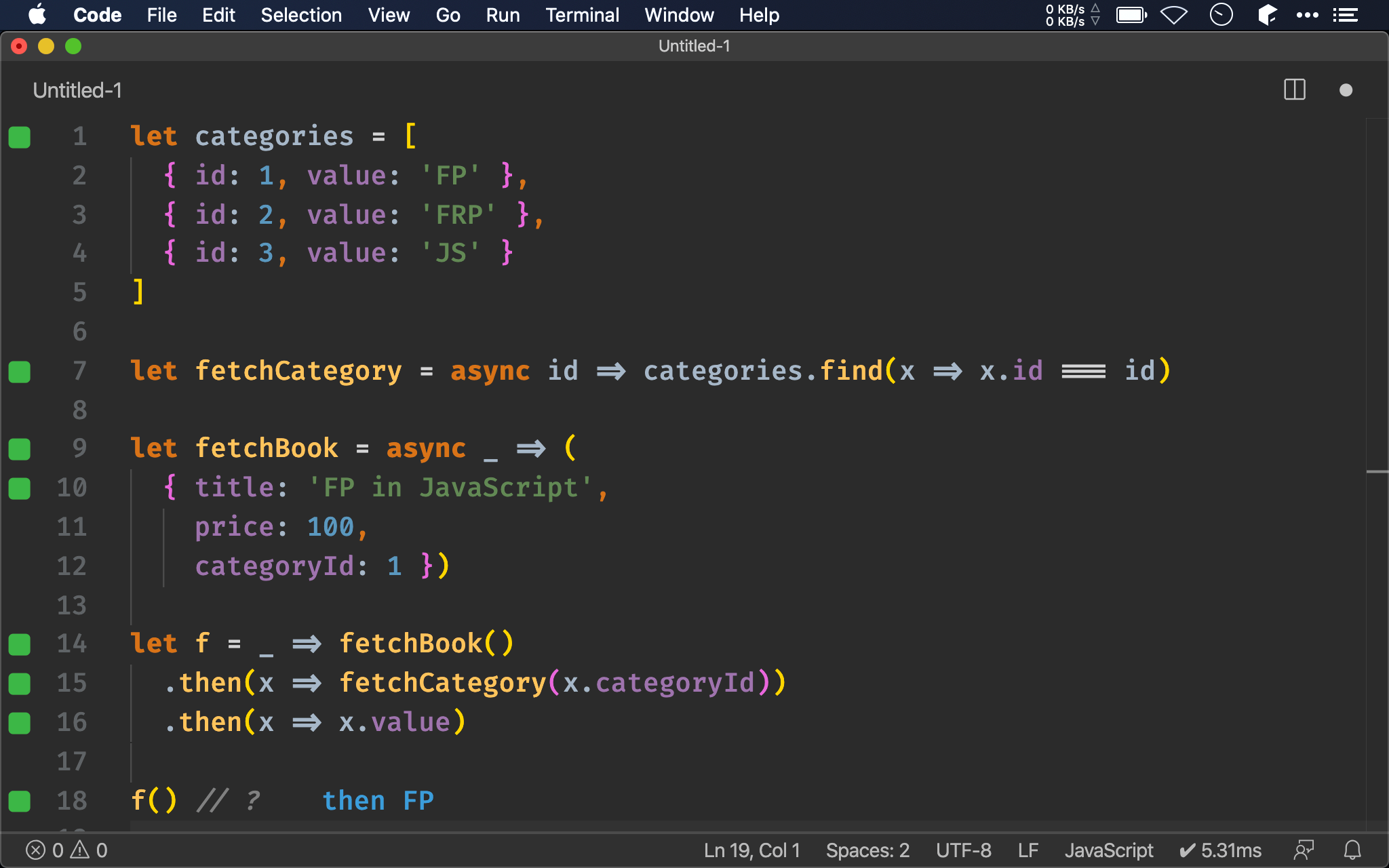
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId))
.then(x => x.value)
fetchCategory() 回傳為 Promise,經過 then() 回傳後理論上會再包一層 Promise,也就是 nested promise,但 Promise 具有 Monad 特性,而 then() 也類似 chain(),可將 nested promise 攤平成一層 Promise,因此不必再使用 nested callback 處理這類 dependent API calls。
Async Await
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
let f = async _ => {
let book = await fetchBook()
let category = await fetchCategory(book.categoryId)
return category.value
}
f() // ?
14 行
let f = async _ => {
let book = await fetchBook()
let category = await fetchCategory(book.categoryId)
return category.value
}
ES2017 支援 async await 後有新寫法,對於回傳 Promise 的 function 可加上 await,它讓每個 Promise 都有 variable 對應,得以使用 sychronous imperative 風格實現 asynchronous,有別於 promise chain 以 function pipeline 實現。
Promise.all()
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => Promise.all([x, fetchCategory(x.categoryId)]))
.then(([x, y]) => [x.title, y.value])
f() // ?
若需求改變,我們不只希望回傳 category 而已,而是同時回傳 title 與 category。
14 行
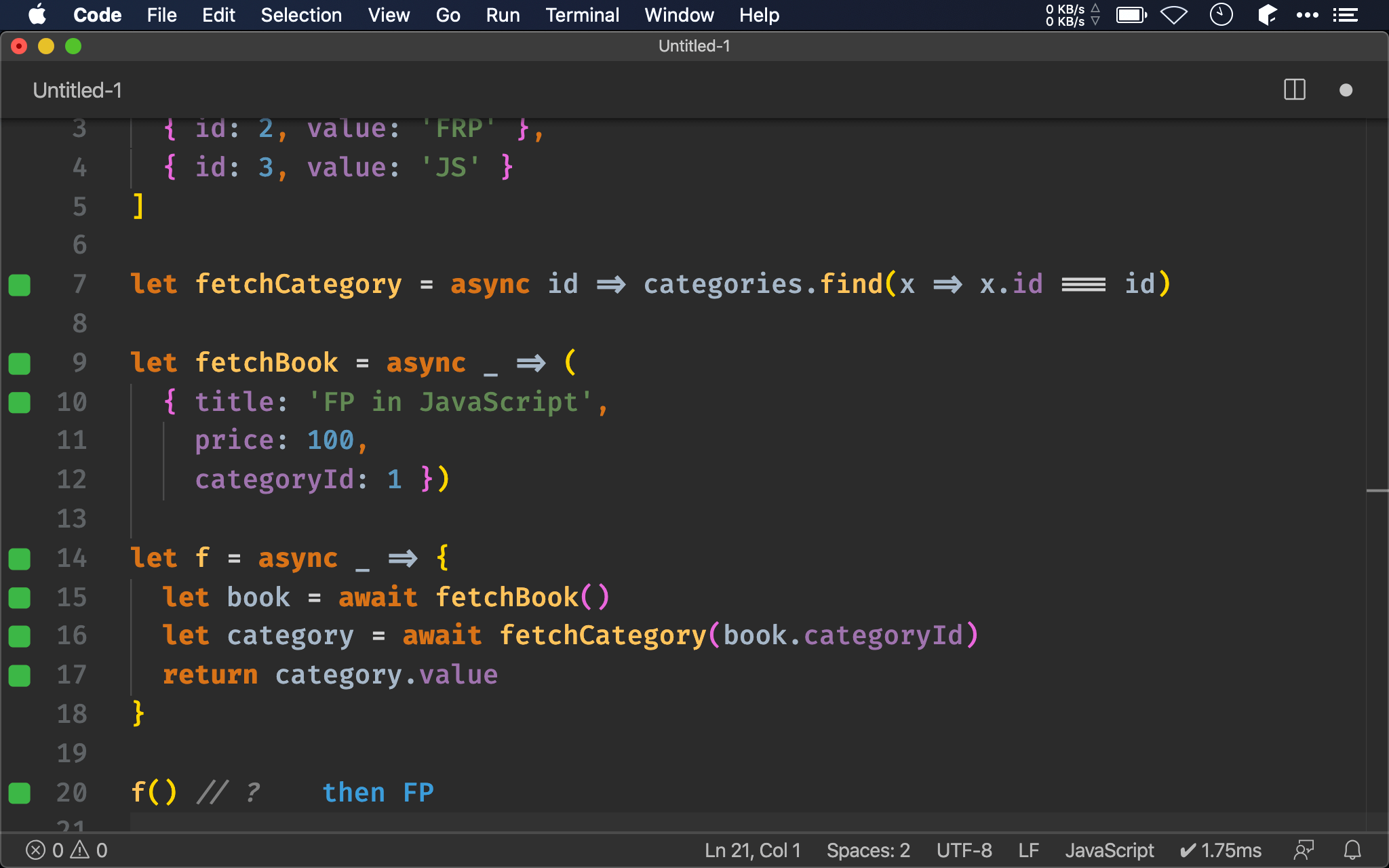
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => Promise.all([x, fetchCategory(x.categoryId)]))
.then(([x, y]) => [x.title, y.value])
title 來自於 fetchBook(),而 category 來自於 fetchCategory(),這對 function pipeline 就比較尷尬,因為橫跨在不同 then() 的 callback 內,彼此看不到對方。
實務上會使用 Promise.all() 將 synchronous 與 asynchronous 包起來傳到下一個 then(),由於 then() 有 chain() 特性,下一個 then() 會將兩層 Promise 攤平並收到兩個 sychronous 值,可用 then() 當 map() 使用整理成 array 回傳。
Side Effect
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
let title = ''
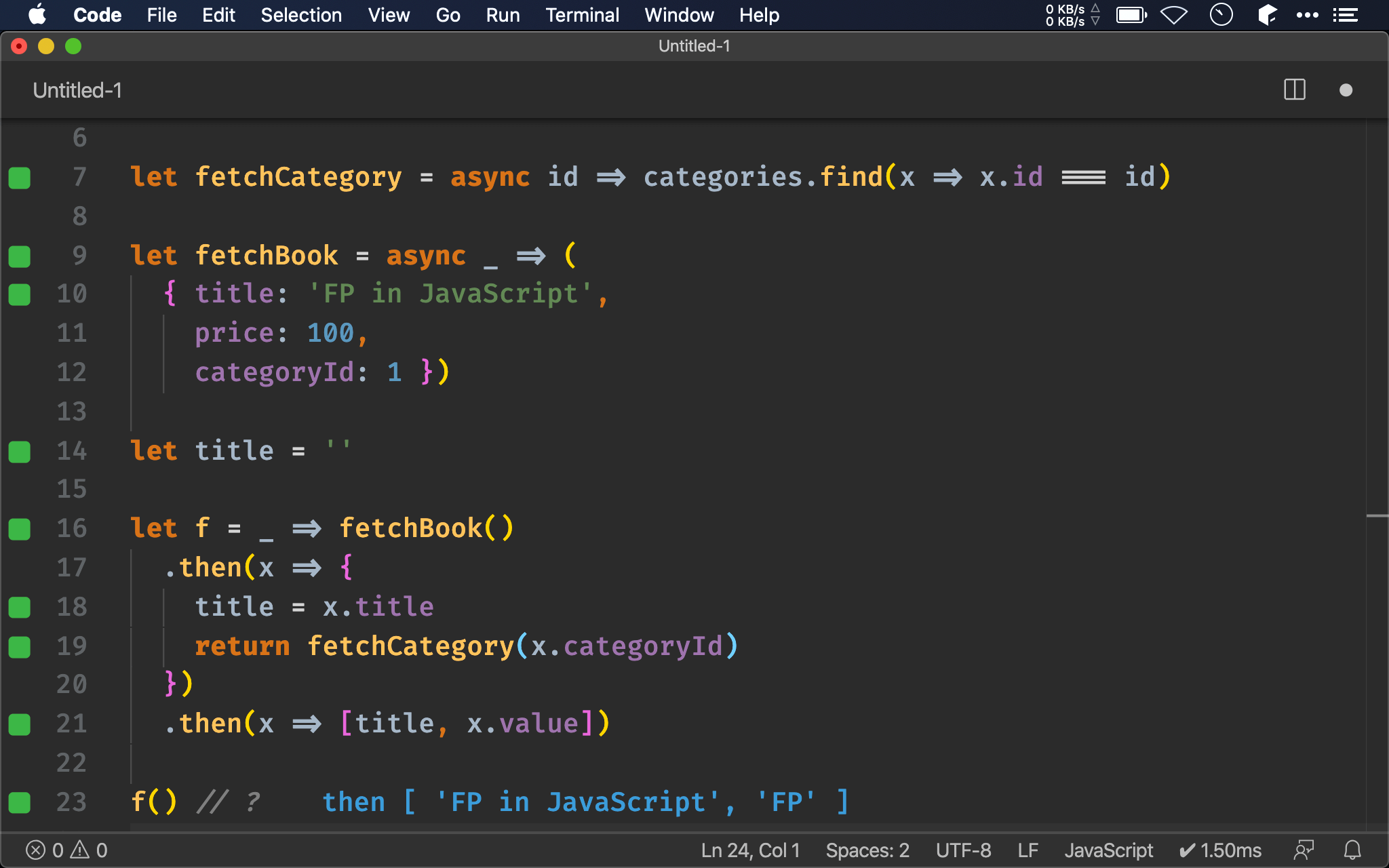
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => {
title = x.title
return fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
})
.then(x => [title, x.value])
f() // ?
14 行
let title = ''
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => {
title = x.title
return fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
})
.then(x => [title, x.value])
另一個方法是簡單使用 side effect 簡單存放 title,如此最後一個 then() 也能讀取到 title。
如 Vue 就是以
data儲存 side effect,因此也可將資料先存放在data,如此整個 promise chain 都能讀取
Nested Promise
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
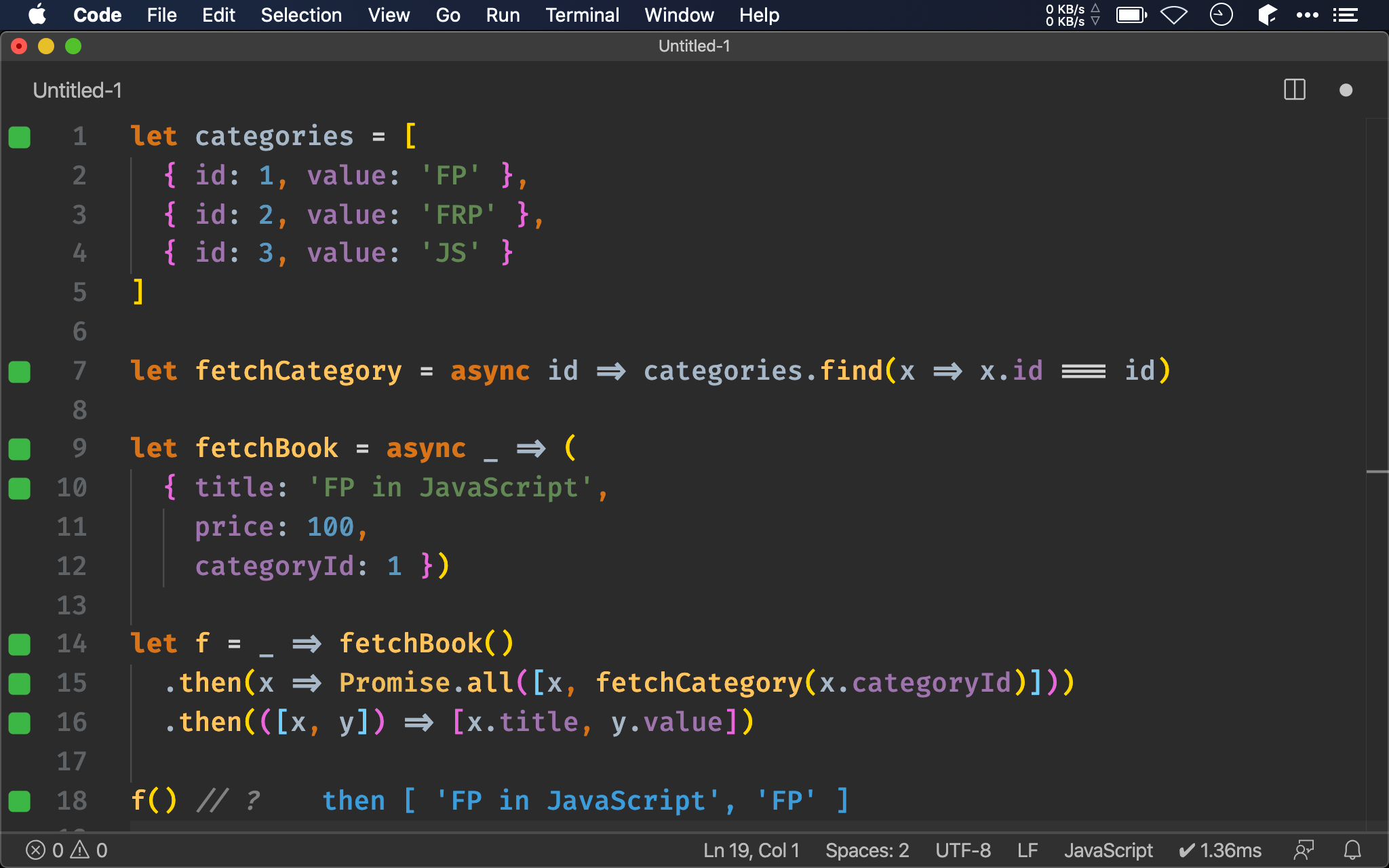
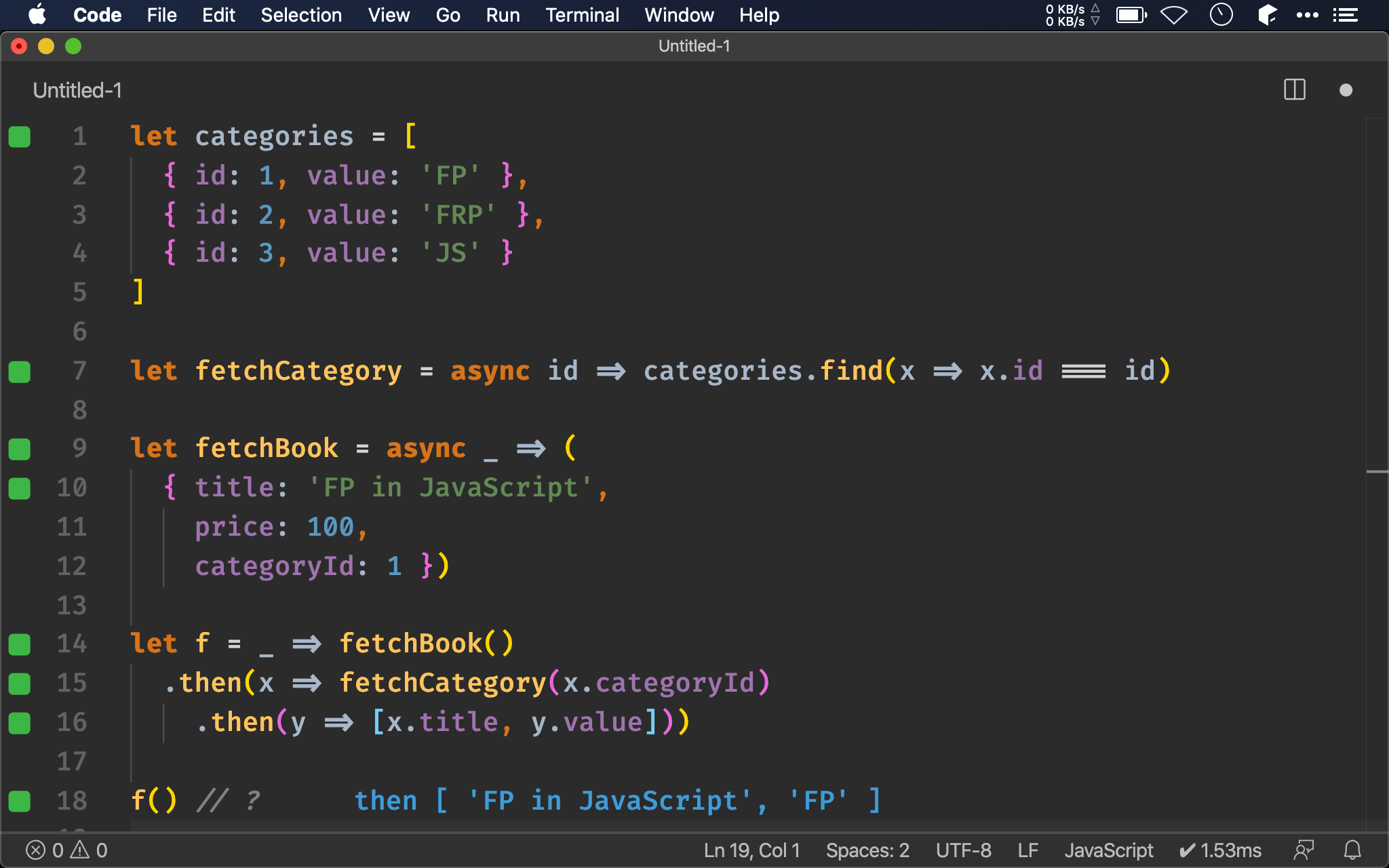
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
.then(y => [x.title, y.value]))
f() // ?
14 行
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
.then(y => [x.title, y.value]))
另一個直覺方法是使用 nested promise,由於 fetchCategory() 的 callback 在內層,因此可輕易讀取到外層 callback 的 x.title。
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id => categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
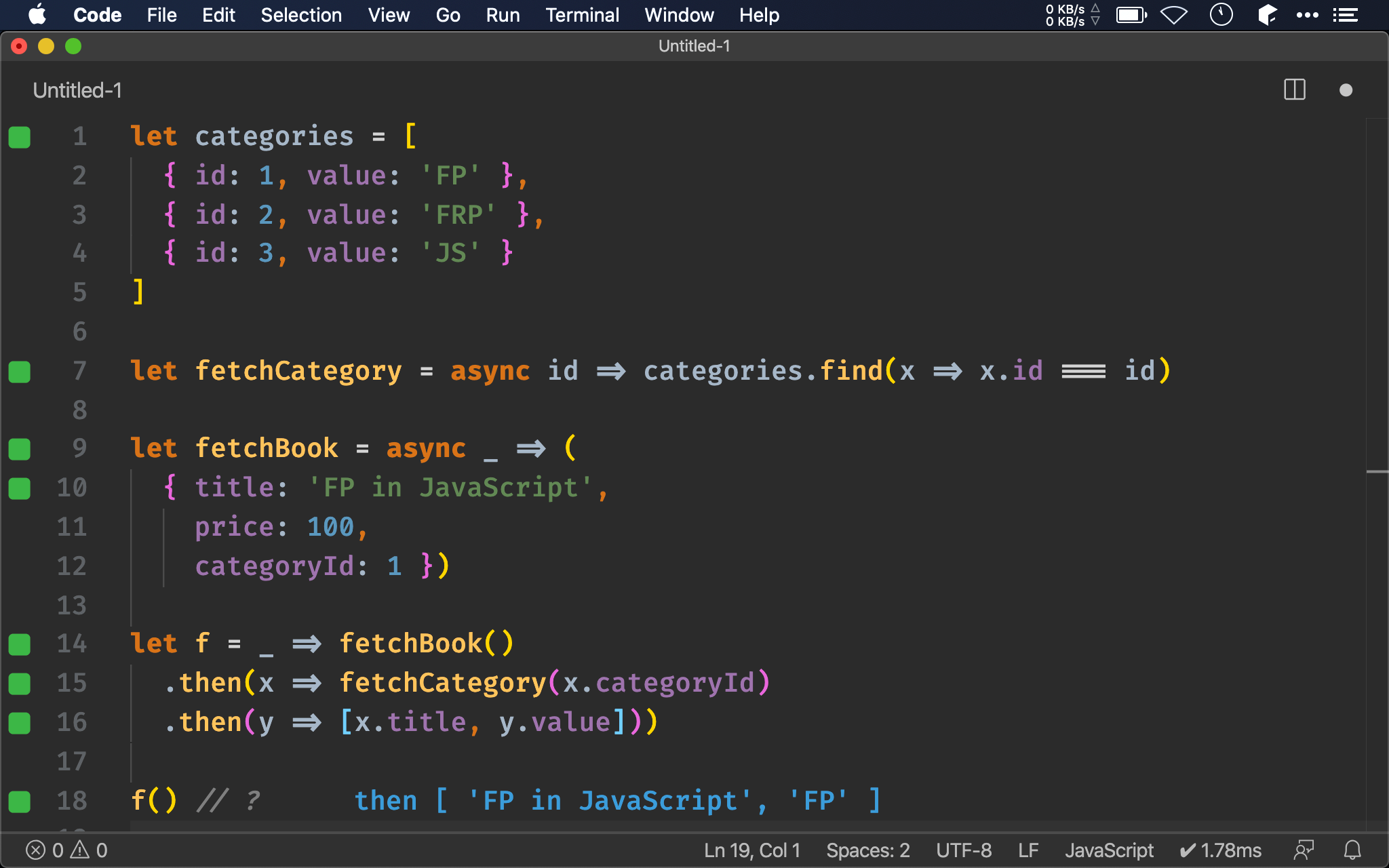
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
.then(y => [x.title, y.value]))
f() // ?
14 行
let f = _ => fetchBook()
.then(x => fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
.then(y => [x.title, y.value]))
Nested promise 看似有 callback hell 味道,其實只要在排版稍動手腳,看起來 then() 也是攤平的,這也是本文所要強調的:nested promise 本身並不邪惡,如本文需求使用 nested promise 就遠本 Promise.all() 簡單易懂。
Async Await
let categories = [
{ id: 1, value: 'FP' },
{ id: 2, value: 'FRP' },
{ id: 3, value: 'JS' }
]
let fetchCategory = async id =>
categories.find(x => x.id === id)
let fetchBook = async _ => (
{ title: 'FP in JavaScript',
price: 100,
categoryId: 1 })
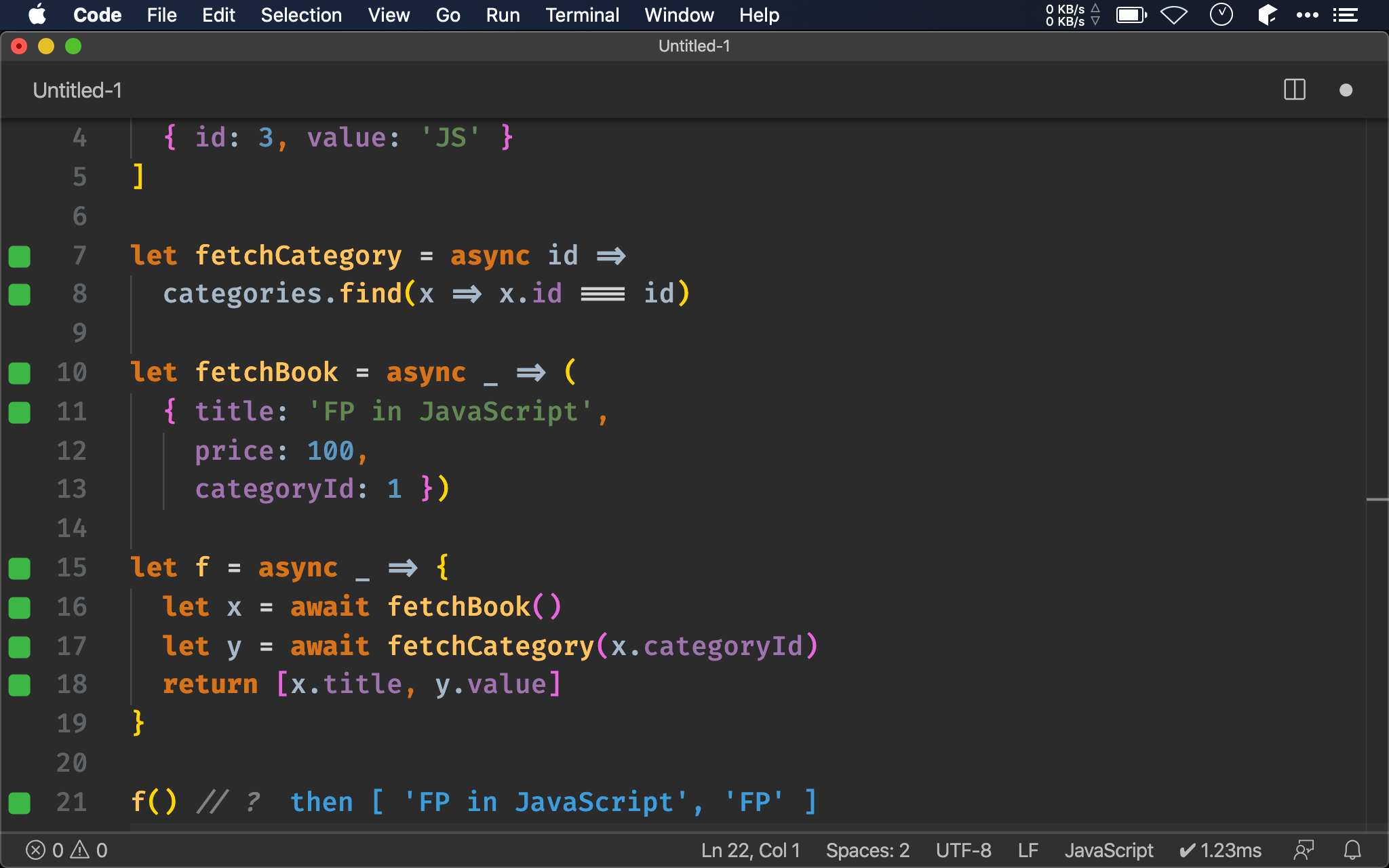
let f = async _ => {
let x = await fetchBook()
let y = await fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
return [x.title, y.value]
}
f() // ?
15 行
let f = async _ => {
let x = await fetchBook()
let y = await fetchCategory(x.categoryId)
return [x.title, y.value]
}
由於 await 會保留每個 then() 的 callback 所回傳 Promise,因此可輕易得到 x.title。
若要說 async await 的優點之一,就是其保留每個 callback 所回傳 Promise,因此後續 expression 可隨時取用,不像 promise chain 的每個 callback 都有自己的 scope,因此要跨 callback 互相存取就很難,所以才必須靠
Promise.all()這種小技巧
Conclusion
- 若想將前一個
then()內的值帶到下一個then()中,使用Promise.all()是 promise chain 慣用手法 - 由於
then()兼具chain()與map()特性,因此 nested promise 並沒有像 nested callback 那樣邪惡,甚至只要透過排版小技巧,nested promise 的可讀性也很高 - 若有 nested promise 需求時,也可考慮使用 async await,由於
await使每個 Promise 都留下 variable,因此特殊需求下時很方便